Changing Gears- India’s Market Reforms
Driving Market Resilience through strategic reforms
- Home
- Changing Gears-India’s Market Reforms
India’s securities market has witnessed a wave of strategic reforms aimed at increasing efficiency, transparency, and investor protection. These reforms, conceptualized by SEBI and driven by MIIs—reflect India’s readiness to align with global best practices while strengthening domestic resilience.
Interoperability was introduced in 2019 across equity cash, equity derivatives, and currency derivatives, allowing participants to clear trades through any designated CCP, regardless of the exchange of execution. This was further extended to Offer for Sale (OFS) in 2020, facilitating seamless inter-exchange settlement.
The reform enables netting efficiencies, improved capital utilization, and margin benefits while reducing trading disruptions and operational fragmentation. Custodians in the equity segment can assign a CCP at the client level, enhancing flexibility.
Overall, interoperability empowers participants with choice, lowers costs, and fosters a unified post-trade experience across markets.
Applicability:
- Equity cash
- Equity Derivatives
- Currency Derivatives
- Offer for sale
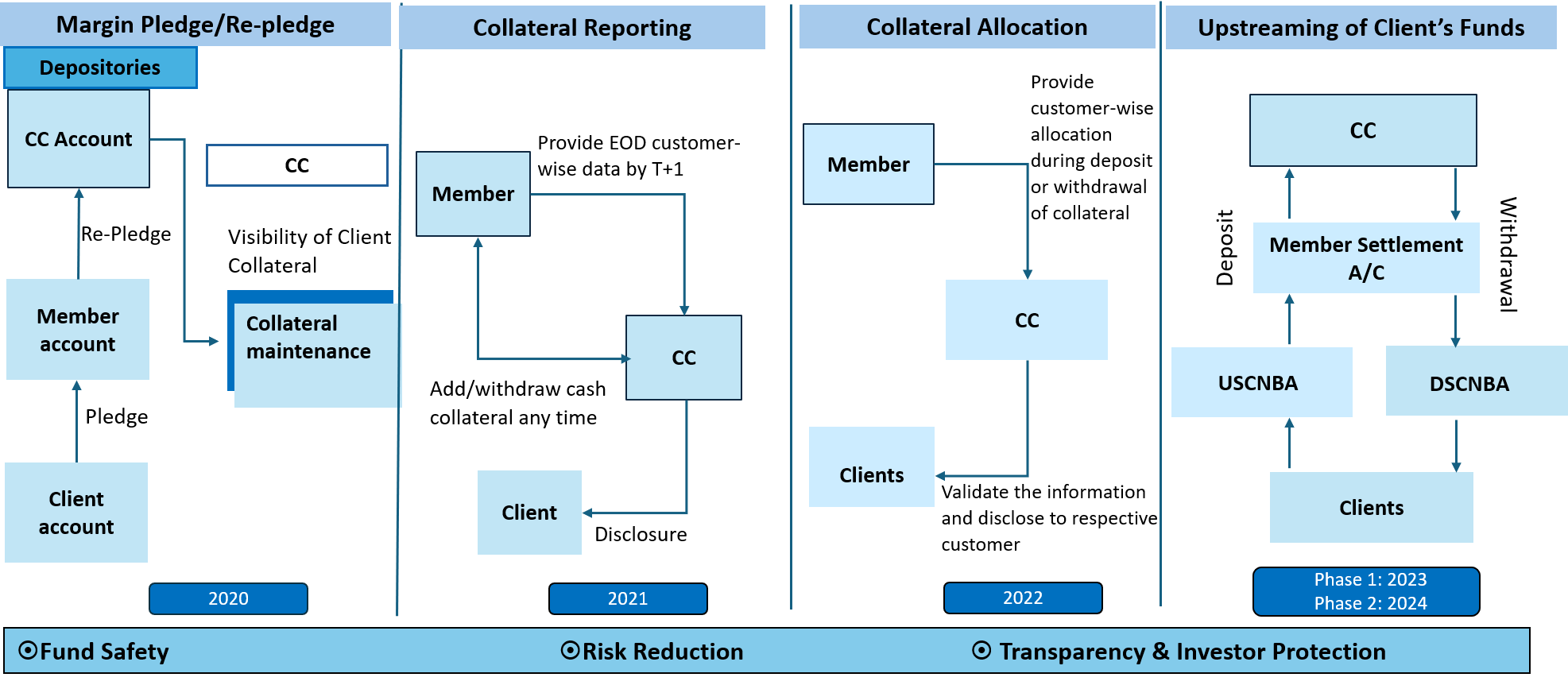
India’s collateral framework has evolved through a series of investor-focused reforms ensuring safety, transparency, and segregation. Beginning with the Margin Pledge-Repledge mechanism in 2020, followed by Collateral Reporting in 2021 and Client-Wise Collateral Allocation in 2022, the system brought client-level visibility and risk containment. The Upstreaming of Client Funds, phased across 2023 and 2024 - mandated that all collateral flows upstream to the clearing corporation, ensuring end-to-end traceability. These reforms significantly reduced fraud and fellow customer risk, enhancing investor confidence. Together, they align with global standards while fortifying domestic market protection.
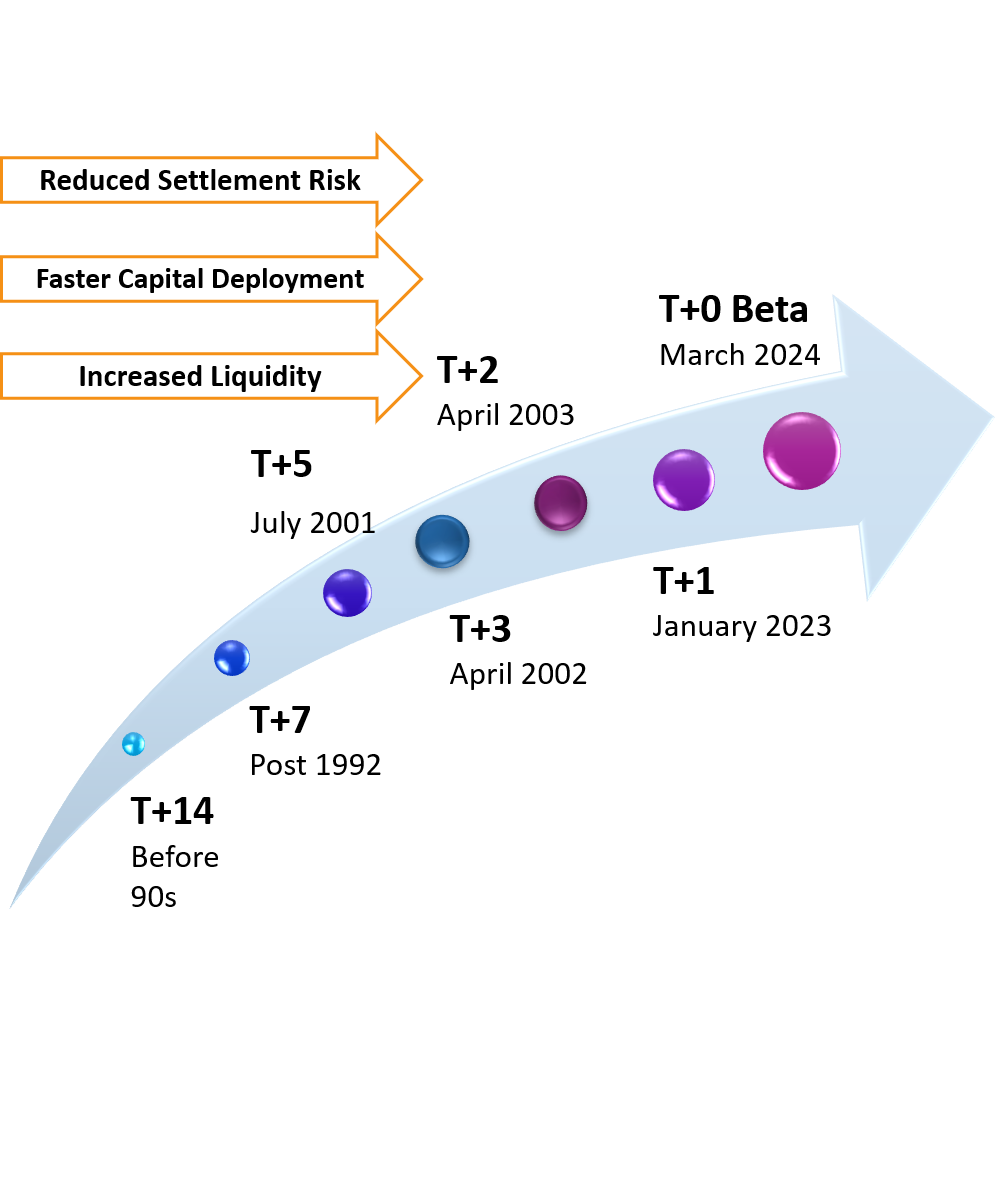
India emerged as a leading market in global settlement reform with its transition from T+2 to T+1 in January 2023 -culminating a journey that began with T+14 in the 1990s. The shift was executed through a phased, collaborative approach that balanced market readiness with systemic resilience.
This reform reduced settlement and counterparty risk, improved liquidity, and enabled faster capital deployment, benefiting both institutional and retail participants. The introduction of an optional T+0 beta model in March 2024 and the custody model integrated February 2025 further reinforces India’s vision toward same-day settlement and setting new standards for efficiency, resilience & investor confidence.
| Activity (Equity cash) | T+1 settlement | T+0 settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Trading hours | T day; 09:15-15:30 | T day; 09:15-13:30 |
| Trade modifications | T day; 16:15 | T day; 13:45 |
| Provisional obligation intimation (Pending trade confirmations) | T day; 17:30 | NA |
| Trade allocation (Identification of custodian for custodian settled trades) | T day; 20:00 | NA |
| Reconciliation and trade confirmation by custodians | T+1 day; 07:30 | T day; 14:45 |
| Final obligation intimation (based on actual confirmations) | T+1 day; 09:00 | T day; 15:15 |
| Securities Pay-in cut off at depositories | T+1 day; 11:00 | T day; 15:30 |
| Funds Payin cut off by clearing member/ custodians | T+1 day; 11:00 | T day; 16:00 |
In a pioneering step toward operational resilience, the CCP SaaS (Software as a Service) model enables seamless continuity of clearing operations by facilitating an immediate shift between two clearing corporations (CC-A and CC-B) in real-time. In case of a disruption at CC-A, and if its DR site is not feasible, the SaaS setup empowers CC-B to take over CC-A’s operations using its own infrastructure, while still maintaining synchronized systems. This world-first CCP framework ensures uninterrupted clearing and risk management during crisis events. Its effectiveness was demonstrated through live market runs on March 2 and May 18, 2024, reinforcing its role in delivering assured continuity and systemic resilience.
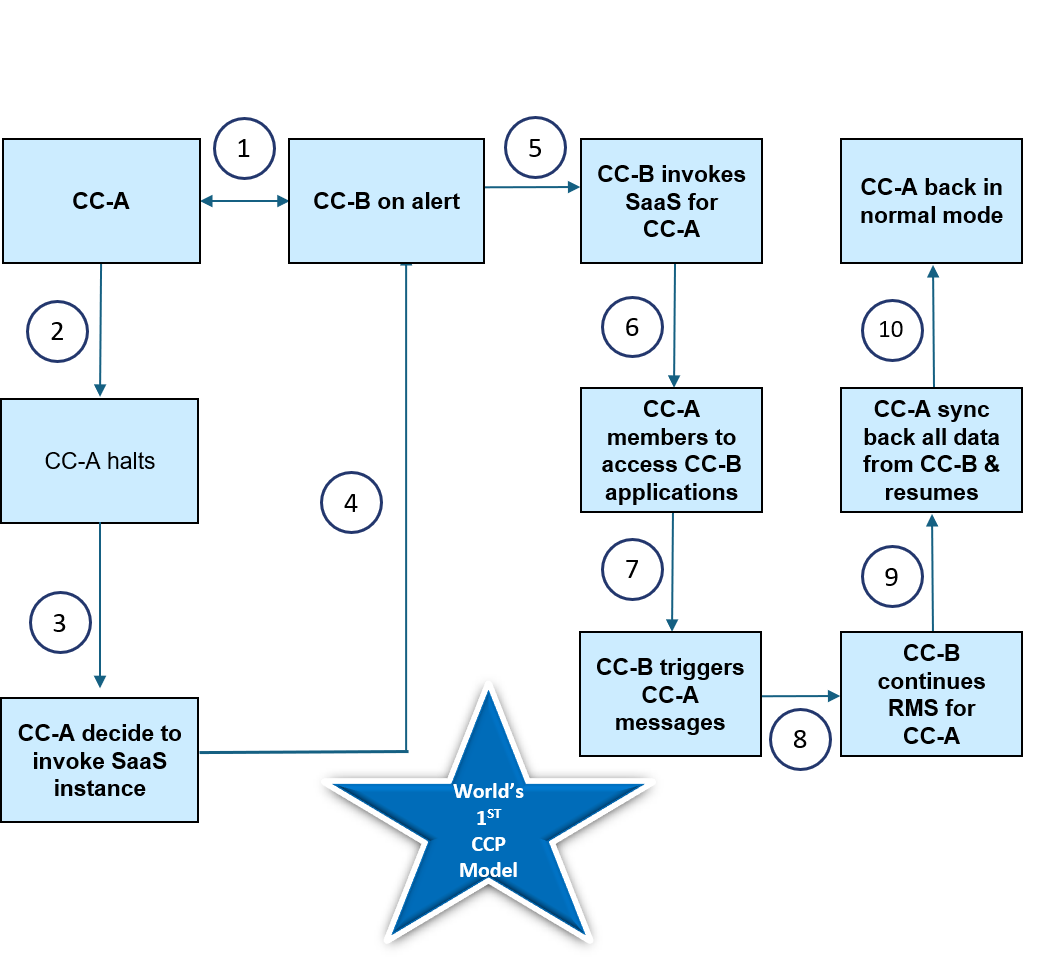
- Normal Day CC-A and CC-B are in sync on real-time basis.
- In the event of a disruption, the impacted CC-A first checks the feasibility of activating its Disaster Recovery (DR) site. If DR activation is deemed non-feasible, the SaaS instance is activated, and the impacted CC-A immediately informs the alternate CC-B
- CC-B seamlessly activates SaaS RMS operations for CC-A in collaboration for the remaining trading session
- During the process, the operations of CC-A functions on CC-B’s software while utilising the hardware infrastructure of CC-A s
- By day’s end, the impacted CC-A resumes & updates its operational data, continuing its normal end-of day processes
- LIVE Market runs conducted on March 2nd, 2024 & May 18, 2024
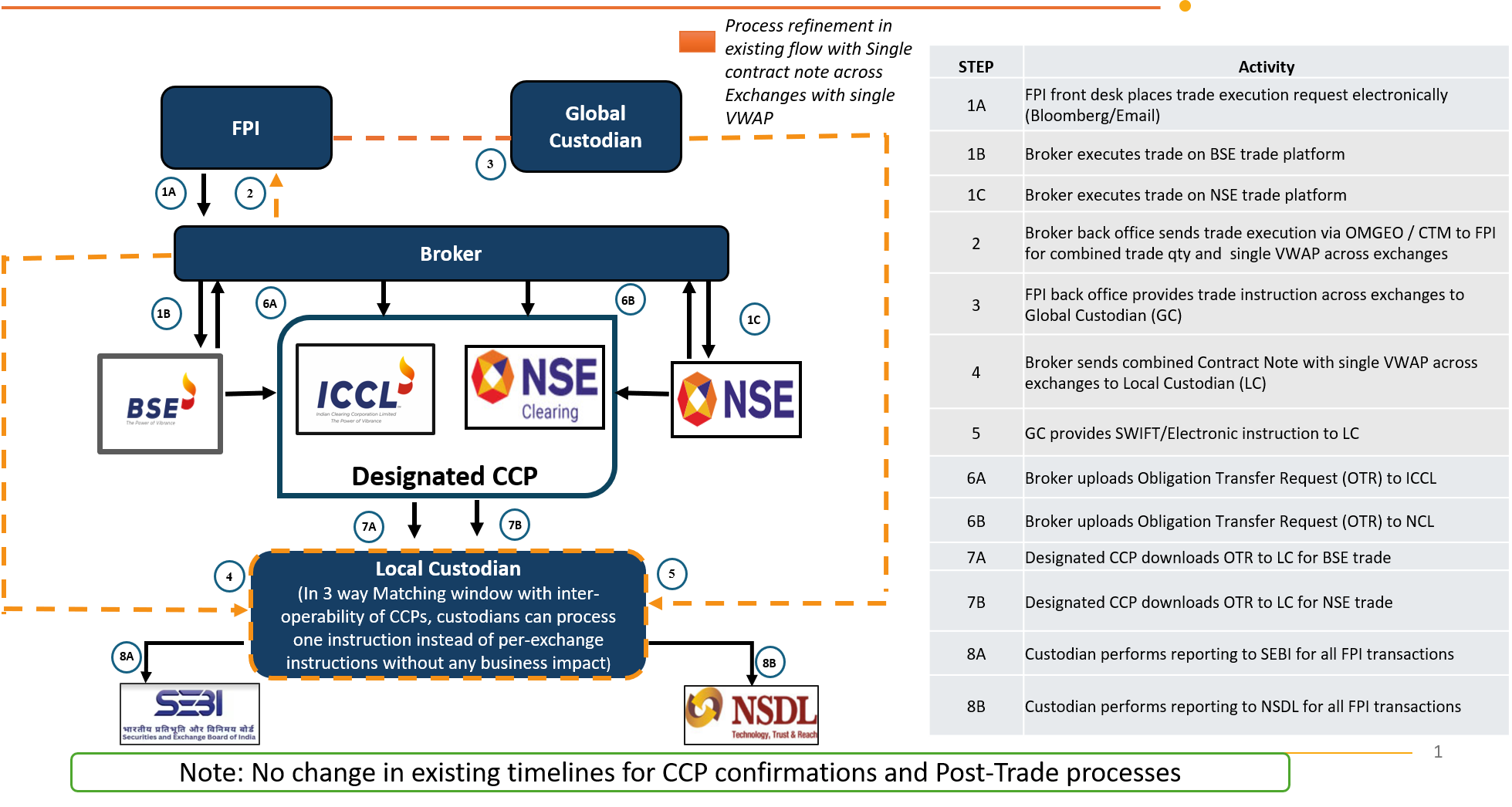
With effect from June 27, 2025, the implementation of the Common Contract Note (CCN) featuring a Single Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) marks a major regulatory stride toward post-trade harmonization. Aligned with the CC Interoperability Framework, CCN integrates trade details across exchanges into a unified, standardized contract note. This reform enhances trade transparency, ensures simplified reconciliation, and reduces regulatory complexity for institutional investors. By enabling cost-efficient, consistent reporting, the CCN initiative reflects collaborative efforts across stakeholders and reinforces India’s commitment to ease of doing business in capital markets.